- The DDX test is a $50 add-on to a regular pesticide test.
- DDX can also be purchased stand-alone for $120.
- DDX testing is voluntary and confidential. You can choose to have the results added to your Certificate of Analysis, or not*. We do not report DDX test results to the seed-to-sale tracking system.
* in order to withhold DDX results from the Certificate of Analysis, the DDX test must be applied as a stand-alone test on an independent sample.
Recently, the Washington State Liquor and Cannabis Board (the LCB) announced the closure of 18 licenses in the Brewster area of the Okanogan valley. In their memo, the LCB briefly explains how they arrived at their conclusion that a small area outside the town of Brewster is uniquely contaminated with a pesticide called DDT, which the LCB assert lays dormant in the soil in that area.
Days later, the LCB announced an emergency rule proposal, with intent to enact those rules without public comment, citing their statutory authority to enact emergency rules for the preservation of public health, safety or general welfare.
DDT Molecular Structure
What is DDT?
DDT stands for “Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane.” It was a popular pesticide in the mid 20th century for the elimination of insects. In the 1960s it started to become apparent that DDT was causing widespread environmental damage. Among other things, evidence showed that DDT was causing the shells of eagle eggs to become too thin which resulted in the death of their hatchlings and measurable declines in their population. In 1972, DDT was banned in the United States. However, its remnants can still be found in some agricultural areas where it was used heavily more than 50 years ago.
DDT is a polychlorinated chemical, meaning it has many chlorine atoms attached. It is readily absorbed in soils where it persists for long periods of time. Slowly over time, DDT breaks down into DDE and DDD, both of which are also damaging to the environment. Collectively, we call all three of these compounds DDX.
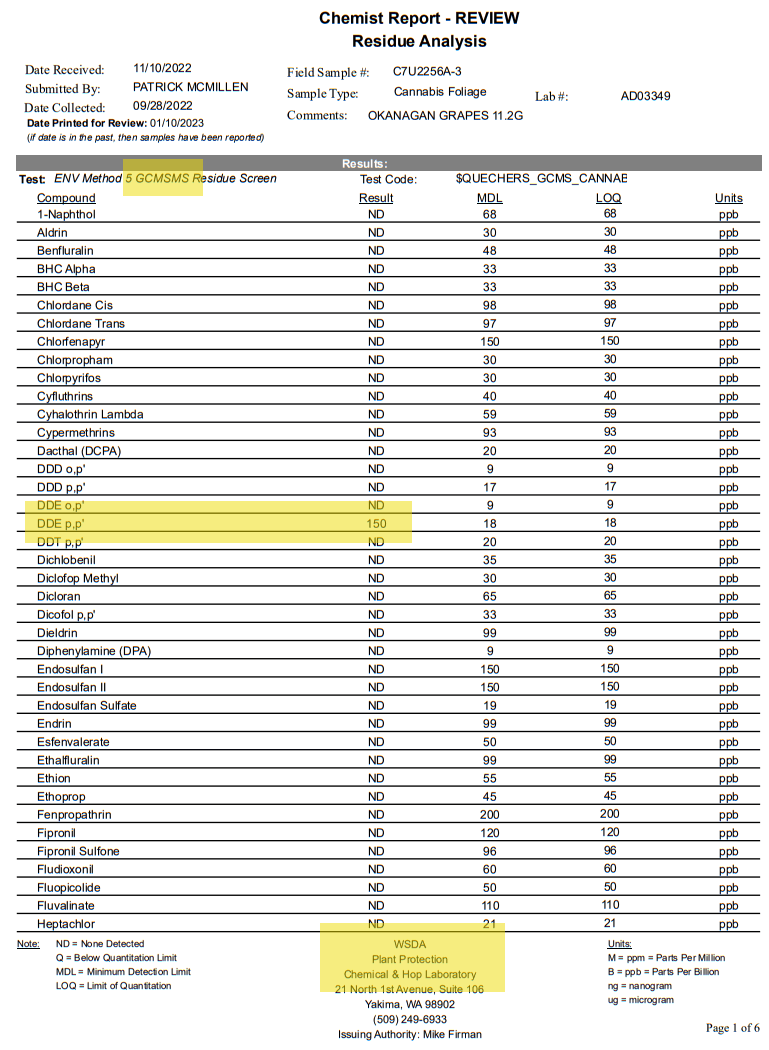
Washington State Department of Agriculture Chemist Report showing detection of DDT breakdown product, DDE, using GCMSMS
How is it tested?
Gas Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (GCMSMS) is the most trusted, most proven technology for chlorinated chemicals such as these1. While it is possible to test for DDX compounds using other technologies, those other technologies lack the ability to detect DDX compounds at low levels2. Comparisons of GCMSMS to other technologies finds that GCMSMS outperforms especially on chlorinated compounds3.
Unsurprisingly, the Washington State Department of Agriculture Laboratory (WSDA), the state-run lab which conducted the testing that resulted in the proposed rules, utilizes GCMSMS for the analysis at their lab. Likewise, Confidence Analytics employs the same technology for analyzing chlorinated compounds, including DDT, DDE, and DDD.
- Luong, et. al., A practical Method for Trave-Level Analysis of Chlorinated Organic Pesticides by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry, LCGC North America, (2012) 30 (4), 342-348 (April issue)
- Sutthivaiyakit, et. al, Confirmatory determination of organochlorine pesticides in surface waters using LC/APCI/tandem mass spectrometry, Anal Bioanal Chem, (2006) 384: 1236-1245
- He P and Aga D. S., Comparison of GC-MS/MS and L-MS/MS for the analysis of hormones and pesticides in surface waters: advantages and pitfalls, Anal Methods, (2019) 11

